Juvenile Justice Research Summary
Youth and Delinquency
Prevalence
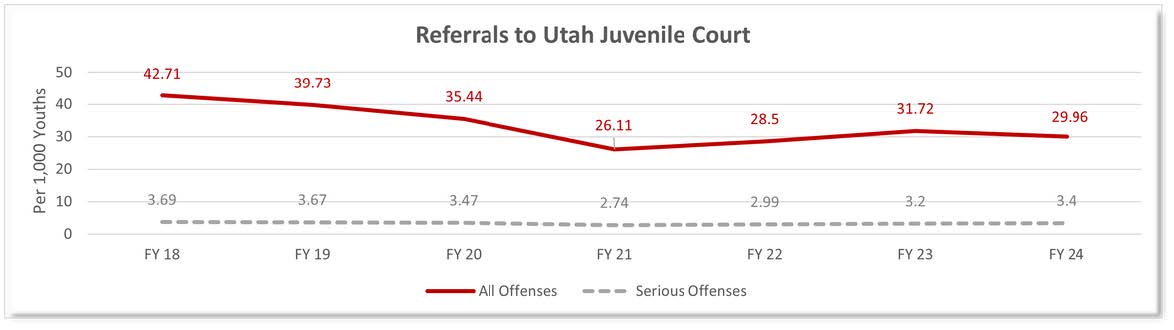
Figure shows the per capita rate per 1,000 youths of serious offenses referred to court, where the serious offense was the most severe charge within an episode by fiscal year.
- In FY 24, youth were referred to the Utah Juvenile Court for serious offenses at a rate of 3.4 per 1,000 youth. Between FY18 and FY24, court referrals for all types of delinquency decreased from 42.71 to 29.6.1
- The number of referrals to the Utah Juvenile Court decreased by 35% between FY 17 and FY24, (4.65 down to 3 per hundred youth.)1
- Between FY15 and FY24, the number of youth in Utah booked for firearm offenses doubled, increasing from 43 to 107.1
- Utah incarcerates youth at one of the lowest rates in the country, with 37 incarcerated youth per 100,000 in 2021 compared to 74 per 100,000 nationally.2
- In 2022, youth accounted for 9.4% of violent crime arrests in the US, compared to 19% in 1994, a 78% decrease.3
Youth Development and Delinquency
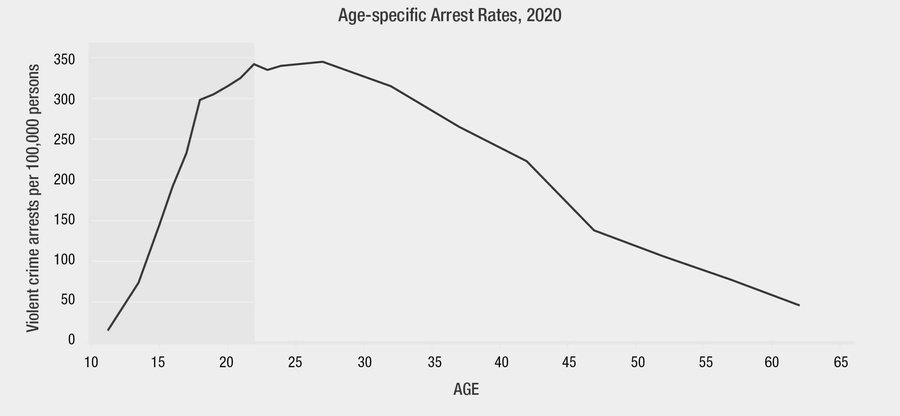
Delinquent behavior peaks in adolescence and early adulthood. Even without formal intervention, delinquency naturally declines over the lifespan, a process called desistance.4
- Even among youth convicted of serious offenses (equivalent to a felony in the criminal justice system), less than 10% go on to have lengthy criminal careers. The vast majority of youth show reduced frequency and severity of delinquency 3 years after their first court involvement.5
Source: National Institute of Justice. (2024) Five things about youth and delinquency.
Figure data from 2020 on age-specific rates shows arrests for violent offenses increased from ages 10 to 22, stabilized from ages 23 to 29, and then declined.
Youth and Gang Involvement
- Among youth in the US, gang membership is less than 2%, peaking at age 14 where approximately 5% of youth report gang involvement.6
- Annually, the number of youth who join gangs in the US (401,000) is similar to the number who leave gangs (378,000).7
- The risk factors for gang involvement are similar to those for delinquent behavior: problems with school and family, antisocial peers, and isolation from pro-social settings. However, rates of delinquency are higher for youth in gangs when compared to similar youth who are not in gangs.8
Characteristics of Effective Treatment
94%
of youth diverted from formal court processing in Utah successfully complete programming1
- The biggest reductions in youth delinquency happen in programs that are community-based, target multiple needs, and improve caregiver skills for communication and monitoring.9
- A leading modality for decreasing youth involvement in the juvenile justice system is multisystemic therapy, which targets criminogenic needs, family functioning, and schools and community support.10
- Formal punishments for delinquency can delay normative developmental processes in instances where the sanction serves to isolate youth from pro-social structures such as family, peers, and school.11
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy reduces anger and aggression in children and adolescents,which can help increase problem solving skills and self-control and decrease delinquency.12
- 94% of youth diverted from formal court processing in Utah successfully complete programming (nonjudicial adjustments) without further court involvement.1